Pickerel Frog- Lithobates palustris |
|||||||
Description
The pickerel frog is sometimes confused with the northern leopard frog. The northern leopard frog looks similar, but its spots are round and randomly scattered on its body, and it doesn't have patches of bright yellow or orange skin on the inside of its thighs. Range |
Habitat
DietThe pickerel frog eats insects, spiders, and other small invertebrates. The pickerel frog tadpole eats algae and plant matter. Life CycleBreeding season runs from March to May. Males gather in breeding pools and call to females with a low-pitched, snore-like call. The female lays an egg mass of up to 3,000 eggs in shallow water. The egg mass is usually attached to submerged vegetation. The tadpoles begin to turn into frogs in about 3 months. In the winter, the pickerel frog burrows into the mud on the bottom of a pond or stream and hibernates. BehaviorThe pickerel frog produces a bad-tasting toxic secretion that protects it from some predators, especially snakes. |
||||||



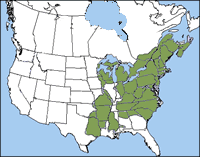 The pickerel frog is found from
southeastern Canada south to South Carolina and northern Georgia, and Alabama and west to Wisconsin, Missouri, Arkansas, and eastern Texas. It is found in New Hampshire.
The pickerel frog is found from
southeastern Canada south to South Carolina and northern Georgia, and Alabama and west to Wisconsin, Missouri, Arkansas, and eastern Texas. It is found in New Hampshire. 