Characteristics
The American badger has a flat body with short legs and a triangular face with a long, pointed, tipped-up nose. It has long brown or black fur with white stripes on its cheeks and one stripe running from its nose to the back of its head. It has small ears on the side of its head and long, sharp front claws
Range
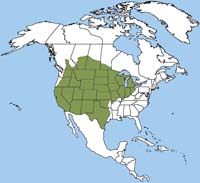 In the United States, the American badger can be found from the west coast to Texas, Oklahoma, Missouri, Illinois, Ohio, Michigan and Indiana. It is also found in southern Canada in British Columbia, Manitoba, Alberta, and Saskatchewan. In the United States, the American badger can be found from the west coast to Texas, Oklahoma, Missouri, Illinois, Ohio, Michigan and Indiana. It is also found in southern Canada in British Columbia, Manitoba, Alberta, and Saskatchewan.
Habitat
The American Badger lives in open areas like plains and prairies, farmland, and the edges of woods.
Diet
 Small burrowing mammals like ground squirrel, rats, gophers and mice make up most of the badger's diet. It digs its prey out of the ground with its strong, sharp claws. The badger will sometimes dig into the burrow of an animal and wait for it to return. Coyotes often will stand by while a badger is burrowing and catch animals that come out of a tunnel trying to escape the badger. The badger also eats snakes, birds and reptiles. It will sometimes bury extra food to eat later. Small burrowing mammals like ground squirrel, rats, gophers and mice make up most of the badger's diet. It digs its prey out of the ground with its strong, sharp claws. The badger will sometimes dig into the burrow of an animal and wait for it to return. Coyotes often will stand by while a badger is burrowing and catch animals that come out of a tunnel trying to escape the badger. The badger also eats snakes, birds and reptiles. It will sometimes bury extra food to eat later. |
|
Life Cycle
 The American badger is solitary, except during the breeding season. The American badger mates between July and August, but the embryos don't really start to grow until December or February. A male badger may mate with more than one female. The American badger is solitary, except during the breeding season. The American badger mates between July and August, but the embryos don't really start to grow until December or February. A male badger may mate with more than one female.
The female gives birth in March. She has 1-5 babies in an underground nest lined with grass. The babies are blind and covered with a thin coat of fur at birth. Their eyes open when they are four weeks old, and they are weaned by the time they are eight weeks old. The young leave their mother when they are 5-6 months old.
Female badgers can mate when they are four months old; male badgers can mate when they are two years old. The American badger lives an average of 4-5 years in the wild.
Behavior
Dens and burrows are a very important part of the badger's life. A badger usually has lots of different dens and burrows. It uses them for sleeping, hunting, storing food and giving birth. A badger may change dens every day, except when it has babies. Badger dens have one entrance with a pile of dirt next to it. When a badger is threatened, it will often back into a burrow and bare its teeth and claws. It may then plug up the burrow's entrance.
 The badger is well-protected from predators. Its muscular neck and thick, loose fur protect it when it is captured by a predator. This gives the badger time to turn on the predator and bite and claw it. When a badger is attacked, it also uses vocalizations. It hisses, growls, squeals and snarls. It also releases an unpleasant musk that may drive a predator away. The badger is well-protected from predators. Its muscular neck and thick, loose fur protect it when it is captured by a predator. This gives the badger time to turn on the predator and bite and claw it. When a badger is attacked, it also uses vocalizations. It hisses, growls, squeals and snarls. It also releases an unpleasant musk that may drive a predator away.
The badger does not hibernate in the winter, but it may sleep for a few days at a time when it is very cold. The American badger spends most of its time on the ground or under the ground, but it can swim, and it even dives underwater.
|